IT项目管理期末复习时整理的笔记
Chapter 1 Introduction to Project Management
Advantages of PM
- Better control of financial, physical, and human resources
- Improved customer relations
- Shorter development times
- Lower costs
- Higher quality and increased reliability
- Higher profit margins
- Improved productivity
- Better internal coordination
- Higher worker morale
A project is
- “a temporary endeavor undertaken to create a unique product, service, or result”
- properties
- a unique purpose
- is temporary
- is developed using progressive elaboration
- requires resources, often from various areas
- should have a primary customer or sponsor
- the sponsor usually provides the direction and funding for the project
- involves uncertainty
PM triple constraint
- Scope
- Time
- Cost goals
- (In reality) -> (Quality)
Project manager
- Provides leadership and direction for the project managers heading the projects within the program
- Suggested Skill for project manager
- The Project Management Body of Knowledge项目管理知识体系
- Application area knowledge, standards, and regulations应用领域的相关知识、标准和规则
- Project environment knowledge项目环境知识
- General management knowledge and skills一般管理知识和技能
- Soft skills or human relation skills软技能/人际关系技能
- 最重要的十大技能和能力(可能考选择题)
- 人际关系技能
- 领导能力
- 善于倾听
- 正直,道德行为,坚定
- 善于建立信任关系
- 口头沟通
- 善于创建团队
- 解决冲突,冲突管理
- 批判性思考,解决问题
- 理解,权衡优先
关于项目管理和项目组合管理
- 项目管理 —— 战术目标
- 项目实施情况
- 计划预期,花费预算
- StakeHolders知道该做什么
- 项目组合管理 —— 战略目标
- 正确的项目?
- 合适的领域投资?
- 有具备竞争力的资源?
- 项目管理 —— 战术目标
PMP (Project Management Profession)
- PMI提供了名为PMP的资格认证
- PMI(Project Management Institute项目管理协会——美国)(知识体系:PMPOK)(认证体系:PMP)
IPMP(欧洲)
Miscellaneous
- 全球生产总值大概有25%花费在项目上
- A program项目群 is a group of projects managed in a coordinated way to obtain benefits which are not available from managing them individually. Many programs also involve elements of ongoing operations
- 项目组合管理 Project portfolio management ///pɔrt’folɪo/
- PMO(Project Management Office)
- 是一个组织内部发挥项目管理协调作用的机构
- 常见作用
- 收集、组织和整合整个组织的项目数据
- 创建并维护项目文档模版
- 开发并提供各种针对项目管理问题的培训
- 为项目经理开发和提供一个正式的职业生涯规划
- 为项目管理提供咨询服务
- 为负责项目和协调项目的项目经历提供一个工作架构
Chapter 2 The Project Management and Information Technology Context
- 9 Knowledge areas
- Core Functions 进度成本范围质量
- Scope management
- Time management
- Cost management
- Quality management
- Facilitating functions 人力采购沟通风险
- Human Resource management
- Communications management
- Risk management
- Procurement management /prə’kjʊrmənt/ 采购
- Project Integration management 集成
- Core Functions 进度成本范围质量
System approach系统方法
- System Philosophy系统哲学
- an overall model for thinking about things as systems
- 将事情作为系统考虑的整体模型
- System Analysis系统分析
- problem solving
- System management系统管理
- address business, technological and organizational issues before making changes to the system
- 用来解决与系统的创建、维持和变更相关的业务上技术上和组织上的问题
- System Philosophy系统哲学
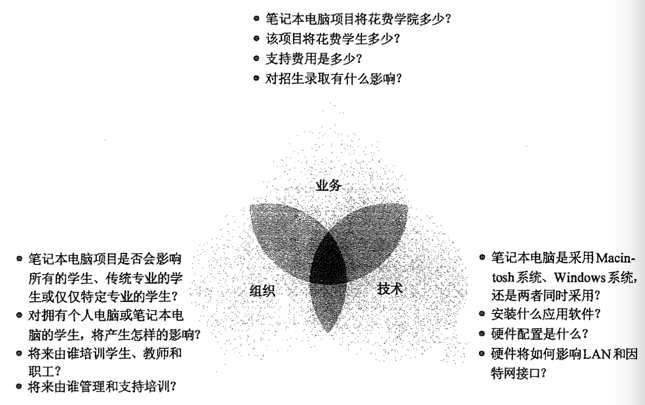
三维模型
- 业务
- 组织
- 技术
四个框架
- Structural frame
- 用来解决组织如何结构化
- Human resources frame
- 重点在于促成组织需求和个人需求之间的平衡和协调
- Political frame
- 组合和人的政治问题——表现为团体和个人为争夺权利和领导地位的竞争。——项目经历必须重视企业的政治和权力问题,了解谁反对谁支持项目
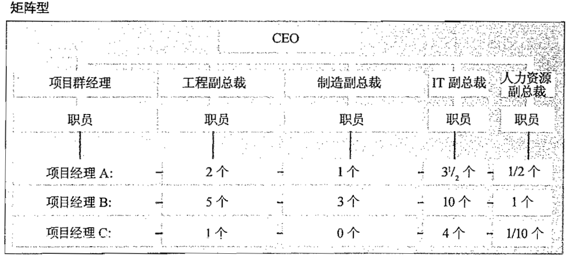
- IT于政治框架有关的主要问题为,从中心职能部门向执行部门,或从职能经理(见matrix图)向项目经理的权利转移
- Symbolic frame
- 主要是指符号和含义
- Structural frame
组织结构
- Functional organizational structure
- Project organizational structure
- Matrix organizational structure
- 组织文化 organizational culture
- 成员认同
- 强调群体
- 关注员工
- 单位整合
- 控制:是要平衡控制的程度以取得好的项目成果而非高控制
- 风险容忍:具有高风险容忍度的组织通常最有利于项目管理
- 奖励标准
- 冲突容忍
- 过程-结果导向
- 基于开放的系统
Phases of the Traditional Project Life Cycle — 4 project phases
- Concept
- Buisness case
- Preliminary cost estimate
- 2-level WBS
- Development
- Project Management plan
- Budgetary cost estimate
- 3+-level WBS
- Implementation
- Last work package
- Definitive cost estimate
- Performance reports
- Close-out
- Completed work
- Lessons learned
- Customer acceptance
- Concept
Product Life Cycles Models
- 有SDLC(sytem development life cycle) 系统开发生命周期—用来描述系统开发不同阶段的一个框架
- A collection of project phases that defines:
- What work — each phase
- What deliverables and when
- Who is involved — each phase
- How management’ll control and approve work produced in each phase
- A deliverable is a product or service produced or provided as part of a project
- Example of predictive life cycle
- Waterfall model
- Spiral model //iterative or spiral approach rather than linear approach
- Incremental build model //progressive development
- Prototyping model
- Rapid Application Development(RAD) model //used to produce sys quickly without sacrificing quality
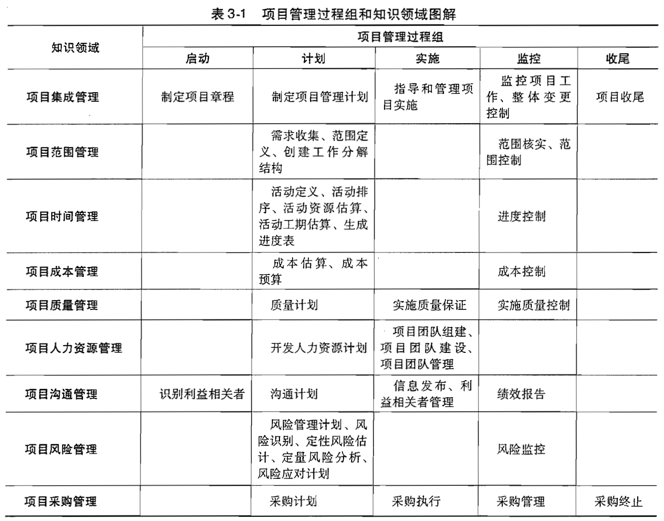
- 项目生命周期和过程组的区别:项目生命周期是一个项目从开始到结束的全过程,大致分为四个阶段:概念阶段、规划阶段、实施阶段、结束阶段。过程组是指完成项目中任何一项任务的五个过程组:启动、计划、执行、控制、结束。也就是说,你可以将一个完整的项目看成是一项任务。但一个项目下面可以很多过程组组成
- 过程组和知识领域关系:
- 知识领域——项目管理过程中设计的业务领域——设计对哪些方面进行管理
- 过程组——某个活动——设计如何管理
- 产品生命周期
- SDLC(Systems Development Life Cycle)
- A framework for describing the phases involved in developing and maintaining information system
- Predictive life cycle: the scope of the project can be clearly articulated and the schedule and cost can be predicted ——前面举例的那些模型
- Adaptive Software Development(ASD) life cycle: requirements cannot be clearly expressed, projects are mission driven and component based, using time-based cycles to meet target dates
- 与前面两个的区别(项目生命周期和五个过程组)
- 产品生命周期:产品生命周期包含通常顺序排列且不相互交叉的一系列产品阶段。
- 它的最后阶段通常是产品的退出,通俗就是产品从生到死的过程。而一个产品从出生和死(退出)却需要经历太多的项目,例如一栋建筑,前期需要调研,中间需要建设然后交付进入生命周期维保,直到这栋大楼拆掉。也就是产品生命周期会含有多个项目生命周期
- SDLC(Systems Development Life Cycle)
3 Basic organization structure ——要知道这三类型的优缺点和能举出这些类型组织结构的实际例子
- Functional
- Project
- Matrix
项目激励方法
- (马斯洛激励理论)需求层次理论:生理需求 安全需求 归属需求 尊重需求 自我实现(塔顶)
Miscellaneous
- 在每个项目阶段后进行管理评审,以便对项目进度、成功的可能性以及项目与商业目标持续的兼容性作出评价。这些管理评审被称为退出阶段Phase Exist或终止点Kill Point
- IT项目的特有问题:项目的性质、项目团队成员的特点和牵涉技术的多样性
- Feasibility 可行性
Chapter 3 The Project Management Process Groups
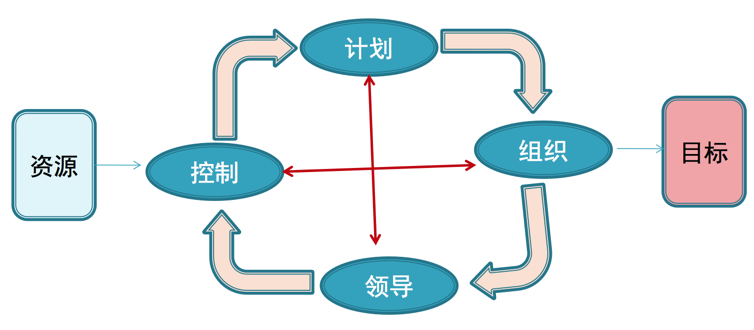
Process 是针对某一特定结果的一系列行动
- A process is a series of actions directed toward a particular result
- Include:
- Initiating processes 定义和授权一个项目或项目阶段
- Develop Project charter
- Identify stakeholders
- Planning processes 包括设计并维护一个切实可行的计划,以确保项目专注于组织的需要
- Purpose: Guide Execution
- Output: team contract, project scope statement, WBS, project schedule, prioritized risks…
- Executing processes (Cost MOST of the time) 包括协调人员和其他资源
- Monitoring and Controlling processes 包括定期测量和检查项目进程以确保项目团队能够实现项目的目标
- Involves measuring progress toward project objectives, monitoring deviation from the plan, and taking correction actions
- Output: performance reports, change requests and updates to various placs
- Closing processes 是对项目或者项目阶段的正式接收,并使之高效率地收尾
- Involves gaining SH&customer acceptance of the final products&services. Even not completed, should be closed out to learn from the past
- Outputs: project files&lessons-learned reports, part of organizational process assets, (final report&presentation)
- Initiating processes 定义和授权一个项目或项目阶段
《项目管理知识体系指南》是一个标准(standard),描述了管理项目的最佳方法
- 方法论(methodology)则描述了该怎么去做事情,并且不同的组织通常有不同的方式
甘特图
- 概要任务, 关键点,里程碑,任务之间的依赖关系:建筑线
WBS
- 最底层为工作包
以下选择可能考内容是否属于某个概念,以及项目可交付成果是项目范围说明而不是项目章程
- Project chapter
- 项目名称
- 项目开始日期&预计完成日期
- 预算信息
- 项目经理信息
- 项目目标
- 做法
- 角色和职责
- Project scope
- 项目名称
- 日期,编写者信息
- 立项理由
- 产品特点和要求
- 项目成果综述
- 项目管理相关交付物
- 产品相关交付物
- 产品成功的标准
- Miscellaneous
- 计划过程组涉及9个知识领域
- 项目小组做经验总结报告来总结项目对在哪里、错在哪里。
- 编制各种项目管理文件都使用模版作为标准格式
- 4 stages of team development
- Forming
- Storming
- Norming
- Performing
- A summary activity in a network logic diagram is often referred to as a. Hammock吊床. Dangler.
- Grade — a category or rank given to entities having the same functional use but different technical characteristics
Chapter 4 Project Integration Management
Processes of Project Integration Management 涉及在整个项目的生命周期中协调所有其他项目的知识领域
- Developing the project charter
- involves
- working with stakeholders to create the document that formally authorizes a project—the charter
- Developing the project management plan
- involves
- coordinating all planning efforts to create a consistent, coherent document — the project management plan
- Directing and managing project work
- involves
- carrying out the project management plan by performing the activities included in it
- Monitor and control project work
- Perform integrated change control
- Close the project or phase
- Developing the project charter
选择IT项目的4个规划阶段
- 进行IT战略规划 —— 将IT战略与组织的整体战略紧密结合起来。识别关键业务领域
- 业务领域分析 —— 记录能从IT中受益的核心业务流程
- 项目计划 —— 定义潜在项目,界定项目范围、收益和约束
- 进行资源配置 —— 选择IT项目,分配资源
NPV (Net present value analysis) !!!
- is a method of calculating the expected net monetary gain or loss from a project by discounting all expected future cash inflows and outflows to the present point in time
- The higher the NPV, the better
- $NPV = \sum_i^n{\frac{(CI-CO)}{(1+i)^t}}$
- CI - 第t年的现金流入量
- CO - 第t年的现金流出量
- i - 折现率
- n - 投资项目的寿命周期
ROI(Return on investment) !!!
- is calculated by subtracting the project costs from the benefits and dividing by the costs
- ROI = (total discounted benefits - total discounted costs)/discounted costs
- The higher the ROI, the better
IRR (Internal rate of return) can be calculated by finding the discount rate that makes the NPV equal to zero
Payback period 回收期——回收总投资的时间
变更控制 — 变更流程要清楚
- 变更输入:项目管理计划、工作绩效信息、变更请求、企业环境因素以及组织过程资产
- 变更输出:更新的状态变更请求、项目管理计划及项目文件
- Objectives
- Influencing the factors that create changes to ensure that changes are beneficial控制可能造成变更的因素以及确保变更都是有益的
- Detemining that a change has occurred确认变更已经发生
- Managing actual changes as they occur管理发生的变更
- 变更控制系统
- 变更控制系统(change control system)是一个正式的、文档式的过程,描述了正式的项目文件可能改变的时间和方式
- 包括:
- 变更控制委员会(change control board, CCB)是一个有权批准或拒绝项目变更的正式的组织机构
- 配置管理(configuration management) 确保了项目管理产品的描述是正确而且完备的
- 变更沟通程序
变更流程
(1)变更申请。应记录变更的提出人,日期,申请变更的内容等信息。
(2)变更评估。对变更的影响范围,严重程度,经济和技术可行性进行系统分析。
(3)变更决策。由具有相应权限的人员或机构决定是否实施变更。
(4)变更实施。由管理者指定的工作人员在受控状态下实施变更。
(5)变更验证。有配置管理人员或受到变更影响的人对变更结果进行评价确定变更结果和预期是否相符,相关内容是否进行了更新,工作产物是否符合版本管理的要求
(6)沟通存档。将变更后的内容通知可能会受到影响的人员,并将变更记录汇总归档。如提出的变更在决策时被否决,其初始记录也应予以保存。
- 大变更
- 建立变更控制系统,包括简历变更控制委员会
- 项目经理和其队员一定要创建一个系统,使每一位受到变更影响的人都能够及时得到信息
- 控制可能发生变更的因素
- 项目经理应该用书面和口头的绩效报告来帮助识别和管理项目变更
- 确认变更已经发生
- 提出变更请求
- 评估变更请求
- 管理那些经过批准的变更的执行过程
- 使用有效的配置管理
- 利用项目管理软件和其他软件,以帮助管理和沟通变更
- 小变更 — 48小时政策
- 受这个变更或者政策影响最大的领域的工作人员可以在48小时内向其上级申请批准。如果因为某种原因觉得项目团队的决定不能实施,接到报告的高管层可以有48小时的时间来更改决定,否则视同接受了项目团队的决定
以下管理出现在分析题
Configuration management 配置管理
- 确保了项目产品的描述是正确而且完备的。这项工作包括识别和控制产品和其支持性文档在功能和物理上的设计特性
- 工作包括
- 确定并记录项目产品的功能和无力设计特征
- 控制这些特征的变更
- 记录并报告变更
- 检查产品以验证是否符合要求
Quality Assurance
- Include all the activities related to satisfy the relevant quality standards for a project
- Another goal is continuous quality improvement
- Benchmarking generates ideas for quality improvements by comparing (specific project practices) or (product characteristics) to those of other projects or products within or outside the performing organization
- A quality audidt is structured review of specific quality management activities that identify lessons learned that could improve performance on current or future projects
质量管理的类型(三种质量管理形式)
- 质量检验型管理
- 全面质量管理
- 质量认证
质量管理四环节
- 质量计划
- 质量保证
- 质量控制
- 质量持续改进
质量保证的活动
- 技术方法的应用
- 正式技术评审的实施
- 软件测试
- 标准的执行
- 修改的控制
- 度量
- 记录和记录保存
国际上软件过程质量管理的三个典型代表
- CMM/PSP/TSP
- ISO900 series
- ISO/IEC15504
Chapter 5 Project Scope Management
范围是指包括生产项目产品及用于生产产品的过程的所有工作
- Project Scope Management Processes
- Collecting requirements
- Defining and documenting the features and functions of the products produced during the project as well as the processes used for creating them
- Defining scope
- Reviewing the project charter, requirements documents, and organizational process assets to create a scope statement
- Creating the WBS
- Creating the WBS: subdividing the major project deliverables into smaller, more manageable components
- Verifying scope
- Formalizing acceptance of the project deliverables
- Controlling scope
- controlling changes to project scope throughout the life of the project
- Collecting requirements
- 范围定义 scope definition
- 就是进一步定义所需开展的工作
- 输出:
- 项目范围说明书和项目文件更新
- 范围核实 scope verification
- 是由stakeholders对已界定的项目范围进行的正式确认。这一确认通常由客户检查完成,然后由关键利益相关者来收尾。
- 范围控制 scope control
- 是指控制项目范围的变更。——用户通常不明确他们想要的系统界面看起来是什么样子或者需要什么功能。。。
- 范围控制的目的就是对那些引起范围变化的因素施加影响,确保变更能依据继承变更控制建立的程序有序地进行,并管理已发生的变更
- 输入:
- 项目管理计划、工作绩效信息、需求文件、需求跟踪矩阵和组织过程资产。
- 主要工具:实施偏差分析
- 偏差(variance)是指计划与实际绩效的差异
- 输出:
- 工作绩效测量结果、组织过程资产更新、变更请求、项目管理计划更新以及项目文件更新
-.-
A work package is a task at the lowest level of the WBS
- WBS是以可交付成果为中心,将项目中所涉及的工作进行分解,定义出项目的整体范围
- 注意层级从1开始数,一般第一层是整个项目,比如课本的内联网项目,第二层才是概念、网站设计、网站开发等等
- 制作方法
- 使用指南
- 类比法
- 自上而下法
- 自下而上法
- 心智图法 —— 通过从一种核心理念发散出来,将思想和想法结构化。
- Dictionary — with WBS — for the reason that the WBS is very concise
- Function: depict the detailed information about the WBS
- Miscellaneous
- 专家评审可以用于所有其他的项目集成管理过程中
Chapter 6 Project Time Management
- Project Time Management Process
- Defining activities定义活动
- Sequencing activities对活动进行排序(依赖关系)
- Estimating activity resources资源估算
- Estimating activity durations活动时间估算
- Developing the schedule进度开发
- Controlling the schedule控制计划

定义活动:里程碑(标注)(不需要估算工期)
- A milestone is a significant event that normally has no duration
活动排序
- 强制 Mandatory dependency
- Inherent in the nature of the work being performed on a project,
- sometimes referred to as hard logic
- Type:
- SS start-to-start
- SF start-to-finish
- FS finish-to-start
- FF finish-to-finish
- 外部 External dependency
- involve relationships between project and non-project activities
- 非强制 Discretionary dependency
- Defined by the project team
- sometimes referred to as soft logic and should be used with care since they may limit later scheduling options
- 强制 Mandatory dependency
估算资源
- 参数估算法
- 三点估算法
三点估算法
- 乐观,悲观,最可能 ==> 最终(乐观+悲观+四倍最可能)/6
PERT Formula and Example
- PERT weighted average = (optimisticTime + 4*mostLikelyTime + pessimisticTime)/6
Critical path
- 要会计算时间 ES, EF, LS, LF
- ES等于所有紧前活动中最后完成活动的最早完成日期,即Max{EFi}
- Total slack or total float(总时差)
- 不耽误整个项目的计划完成时间的前提下,一项活动从它最早开始算起可以推迟的时间 — LF-ES?
- Free slack or free float(自由时差)
- 不耽误其任何紧后活动最早开始的前提下,一项活动能够推迟进行的时间
- 要会计算时间 ES, EF, LS, LF
资源分解结构(resource breakdown structure RBS)
- 是一种根据类别和类型来识别项目资源的层次结构。
- 例如资源类别中可能包括分析师、程序员和检验员
- 制定项目计划的内容(很重要) 6.5的内容
- 工期(duration)
- 等于开展活动的实际时间+占用时间
- 例如尽管可能只花一周就能完成一项实际的工作,但估计的工期可能是两周,目的是根据外部信息留出一些额外的时间进行调整。
- 分配的资源也会影响工期估计
- 人工量(effort)
- 是指完成一项任务所需(多少个单位)的工作天数和工作小时。
- 工期(duration)
七个图的内容(必考答题)计算答题, eg. IPMP认证考试
Terminology
- AOA (Activity-on-arrow)双代号网络图法或箭线图法(arrow diagramming method, ADM)——一种网络图技术,箭线代表活动,节点用来连接活动
- PDM (Precedence diagramming method)是一种用方框表示活动的网络图技术。——就是MS project生成的那种
- Dummy activities
-是指没有工期和资源需求的活动,有时偶尔在双代号网络图中,用来辅助表示活动间的逻辑关系 - SMART标准
- 按照该标准,里程碑应该
- Specific 具体
- Measurable 可测量
- Assignable 可分配
- Realistic 符合实际
- Time-framed 有时间限制
- 按照该标准,里程碑应该
- 甘特图:一种用于显示项目进度信息的常见工具
- 黑色钻石:里程碑;白钻石为延误的里程碑
- 两端带箭头的黑色粗线:总结性任务
- 浅灰色的水平线条代表了每项任务的工期
- 连接这些符号的箭线代表任务间关系
- 追踪甘特图 : 显示项目世纪进度信息的特殊甘特图,用于评估项目进度(比较了原计划项目进度信息和实际项目进度信息)
- 关键路径分析:一种用于设定和控制项目进度的重要工具
- 关键链进度安排法:当编制项目进度表时,这种技术主要考虑如何使用有限的资源
- 计划评审技术(PERT)分析:一种评估项目中进度风险的工具
Chapter 7 Project Cost Management
计算题考得多
- Project Cost Management Processes
- Estimating costs 成本估算
- Developing an approximation or estimate of the costs of the resources needed to complete a project 涉及找出完成项目所需资源成本的近似值或估计值
- Determining the budget 制定预算
- Allocating the overall cost estimate to individual work items to establish a baseline for measuring performace 涉及将总体成本分配给各个工作包
- Controlling costs
- Contolling changes to the project budget 涉及对项目预算变更的控制
- Estimating costs 成本估算
- 质量成本(cost of quality) = 一致成本 conformance + 不一致成本 nonconformance
- Cost of conformance
- 是指交付符合需求并合适使用的产品。这种成本的例子包括与制定质量计划相关的成本,分析并管理产品需求的成本以及测试的成本
Cost of nonconformace
- 意思是对失败负责或因没有达到预期质量所造成的成本
直接成本
- 是与生产项目产品和服务直接相关的成本。你可以把直接成本直接归结到某一项目上去。例如,项目中全职工作的工人的工资和为项目专门购买的软硬件都是直接成本。项目经理应该关注直接成本,因为这是可控的
- 间接成本
- 是不与成产项目产品和服务直接相关的成本,但它间接地和完成的项目相关。例如,在一座大楼上,有为不同项目工作的1000名职工,那电费、毛巾都是间接成本。间接成本可以被分摊到项目中去,但是项目经理几乎无法控制它们
EVM (Earned Value Management)
- EVM is a project performance measurement technique that integrates scope, time, and cost data
- Given a baseline(original plan plus approved changes), you can determine how well the project is meeting its goals
- You must enter actual information periodically to use EVM
More and more organizaitons around the world are using EVM to help control project costs
Some Terminologies
- PV plan value 计划值
- Alias — Budgeted Cost of Work Scheduled(BCWS) | Budget
- is that portion of the approved total cost estimate planned to be spent on an activity during a given period
- AC actual cost 实际成本
- Alias — Acutal Cost of Work Performed(ACWP)
- is the total of direct and indirect costs incurred in accomplishing work on an activity during a given period
- EV earned value 挣值
- Alias — Budgeted Cost of Work Performed(BCWP)
- an estimate of the value of the physical work actually completed
- EV = PV to date * RP
- RP(rate of performace)绩效比率
- 如果这周计划安装一个服务器,但实际只安装了一半,那么RP就是50%
- !关于偏差和指数
- 偏差 = EV-实际或计划值
- 指数 = EV/实际费用或计划值
- CV(cost variance)成本偏差
- 挣值减去实际费用 EV-AC
- 若为负数意味着完成的花费比原计划的多
- SV(schedule variance) 进度偏差
- 挣值减去计划值 EV-PV
- 若为负数意味着完成工作花费了比原计划更多的时间
- CPI = EV/AC cost performance index 大于1则说明花费低于预算
- SPI = EV/PV 若都<1 则存在偏差 scheldule performace index 大于一则说明项目超前于预期
- BAC(Buget at completion) 完工预算—这个项目最初的总预算
- Estimate at Completion(EAC) = BAC/CPI
- Estimated Time to Complete = Original Time Estimate/SPI 完成估计时间=开始时间估计/SPI
- PV plan value 计划值
- Terminology
- Learning curve theory 当重复生产物品时,在一个固定模式下,单位成本随生产数量的增多而下降
- Reserve储备
- 应急储备 contingency 考虑可以部分预测到的未来情况 known unknowns,比如组织知道信息技术人员有20%人员更替,则为信息技术人员支付雇佣和培训成本
- 管理储备 management 考虑不确定的未来情况,unknown unknowns,比如一个项目经理病了或者失去一个重要的供应商
Chapter 8 Project Quality Management
目的是为确保项目满足承诺的需求
Three Process
- 质量规划 quality planning
- 实施质量保证 performing quality assurance
- 实施质量控制 performing quality control
因果图或鱼骨图 (cause&effect diagrams/fishbone diagrams)
- 定位质量问题的原因
- 5way法,即不断地问为什么
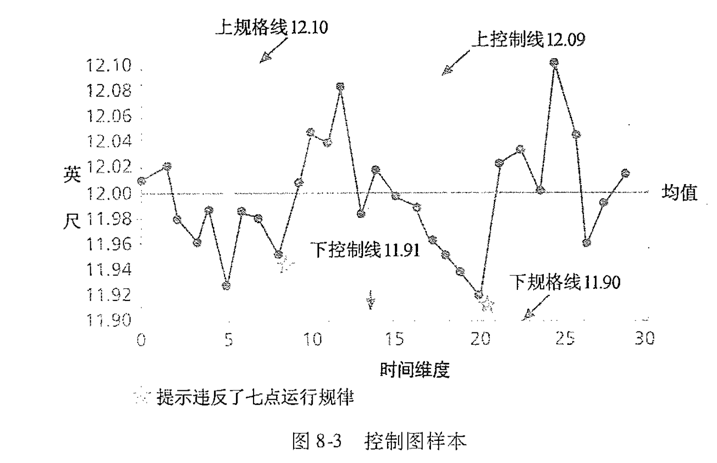
控制图 control chart
- 实时展示项目进展信息的图表
- 七点运行定律(seven run rule),如果在一个质量控制图中,一行上的7个数据点都低于平均值或者高于平均值,或者都是上升的或者都是下降的,那么这个过程就需要因为非随机原因而接受检查
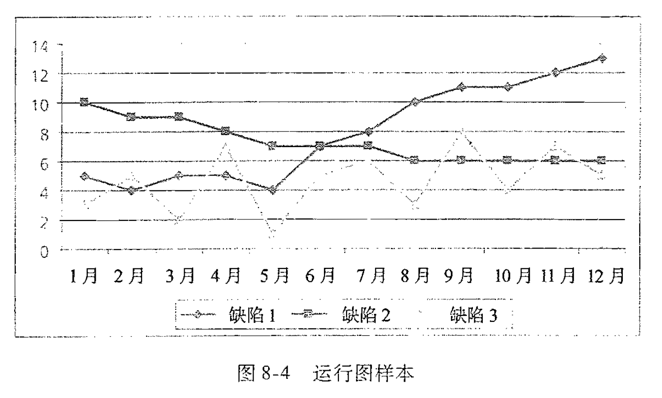
运行图 run chart
- 是一个展现一个过程在一段时间的历史和变化情况的模型,是一个按发生顺序画出数据点的线性图标
- Example:将三种不同类型的缺陷按照每月的缺陷数来绘制成图
散点图 scatter diagram
- 用于显示两个变量之间是否有关系
柱状图 histogram —一个变量分布的条状图
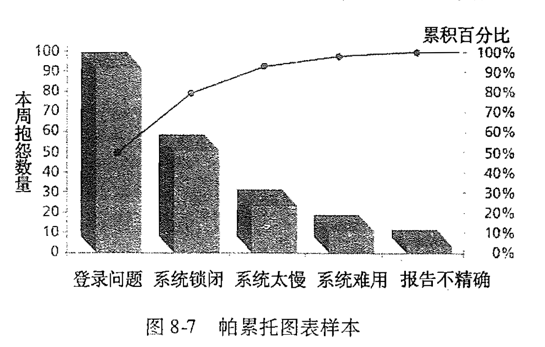
帕累托图标 (Pareto chart) 二八图
- 一个帮助鉴别问题和对问题进行优先排序的柱状图
- Pareto analysis 帕累托分析 80-20定律
- 意思时说80%的问题通常是由20%的原因造成的
- Example 第一个问题的抱怨占总抱怨量的55%,那么第一个第二个问题的抱怨累加起来占到80%,意思是这两个领占抱怨量的80%
Software Test
Type of Tests
- Unit test
- 是测试每一个单个部件(通常是一个程序),以确保它尽可能没有缺陷。应在集成测试之前进行
- Integration test
- 发生在单元测试和系统测试之间,检验功能性分组元素。它保证整个系统能正常工作
- Test Functionally grouped components
- System test
- 是指作为一个整体来测试整个系统。它关注宏观层面,以保证整个系统能正常工作
- Test the entire system as one entity
- user acceptance test
- 发生在接受系统交付之前,是由最终用户进行的一个独立测试。它关注的是系统对组织的业务适用性,而非技术问题
- Unit test
CMMI (Capability Maturity Model Integration)
- 能力成熟度模型集成
- 是“一种为组织的有效过程提供基本要素的过程改进方法。它可用于指导一个项目、一个部门或整个组织中的过程改进。CMMI有助于集成传统上分离的组织功能,设定过程改进目标和优先顺序,提供质量过程指导,为评估现有的过程提供一个参考点”。
- 能力层次:
- 0 不完整级:部分实施了过程,无通用目标
- 1 已执行级:
- 2 受管理级
- 3 已定义级:过程被严格地进行了定义。其标准过程描述及程序已经从组织的系列标准过程中分离出来,以适应这一特殊项目
- 4 定量管理级
- 5 持续优化级
Chapter 9 Project Human Resource Management
人力资源管理
- 马斯洛的需求层次理论: Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
- 生理需求
- 安全需求
- 社会认可
- 尊严自我实现
资源平衡(resourceleve1ing)是通过推迟任务来化解资源冲突的一种方法
Chapter 10 Project Communications Management
计划(确定及准备信息)发布、绩效报告,SH管理
- communications planning
- 包括确定项目利益相关者所需的信息和沟通需要:谁需要什么信息,什么时候需要,信息如何传递给他们等
- information distribution
- 包括使项目利益相关者能通过适当的方式获得所需的信息
- performance reporting
- managing stakeholders
计算沟通渠道数量:
- communications channels = $\frac{n*(n-1)}{2}$
A status report describes where the project stands at a specific point in time
Chapter 11 Project Risk Management
项目风险管理
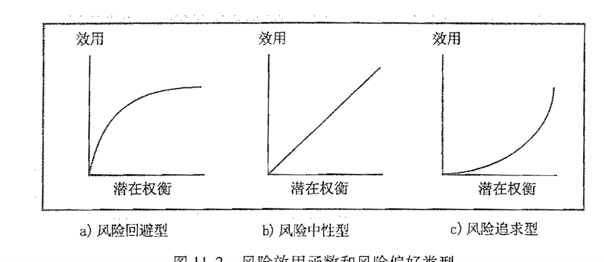
Risk utility or risk tolerance is the amount of satisfaction or pleasure received from a potential payoff
- Risk-averse风险回避
- Risk-seeking风险偏好
- Risk-neutral风险中立
contingency plans <——> fallback plans
例如,一个大学毕业生会有一个毕业后将在哪儿生活的主计划和几个应急计划,但是如果这些计划都无法奏效的话,就会有个退路计划:先在家住一段时间。有时,应急计划和退路计划这两个词可以互换使用。
德尔菲法/得尔飞法(Delphi Method)
德尔菲法依据系统的程序,采用匿名发表意见的方式,即专家之间不得互相讨论,不发生横向联系,只能与调查人员发生关系,通过多轮次调查专家对问卷所提问题的看法,经过反复征询、归纳、修改,最后汇总成专家基本一致的看法,作为预测的结果。这种方法具有广泛的代表性,较为可靠。
风险登记单(risk register) 就是一份文档,包含了各种风险管理过程的输出,通常以表格或电子数据表格的形式出现。它是一种把潜在风险事件和相关信息文档化的工具。
EMV 必考
- Expected monetary value(EMV) is the product of a risk event probability and the risk event’s monetary value
EMV = 概率(P) X 产出

- SOW statement of work 工作说明:是对采购所需工作的描述
- 采购文件
- 需求建议书或建议请求书(RFP,request for proposal)是一份用来请求未来供应商提交提案的文件
- 报价请求书(RFQ,request for quote)是请求期望的供应商报价(投标bid)的文件
oursourcing(外包)
— 管理合同或者合同管理,是保证供应商的执行结果满足合同的要求
- Cost-reimbursable contracts
- cost plus incentive fee contract, CPIF contract 节省的成本费用按照比例分层
- cost plus fixed fee contract, CPFF contract,除了执行成本,还要支付一个根据估算成本百分比得到的固定费用
- cost plus award fee contract, CPAF contract(卖方满足了客观执行标准的基础)—— 比如饭店给小费,但仍需为食物付费
- cost plus percentage of costs contract, CPPC contract 除了支付执行成本外还支付按总成本一定比例的费用。这时买方承当了所有风险,反而激励了供应商增加成本。为美联邦政府所禁止